Understanding Cauda Equina Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Nonsurgical Treatment
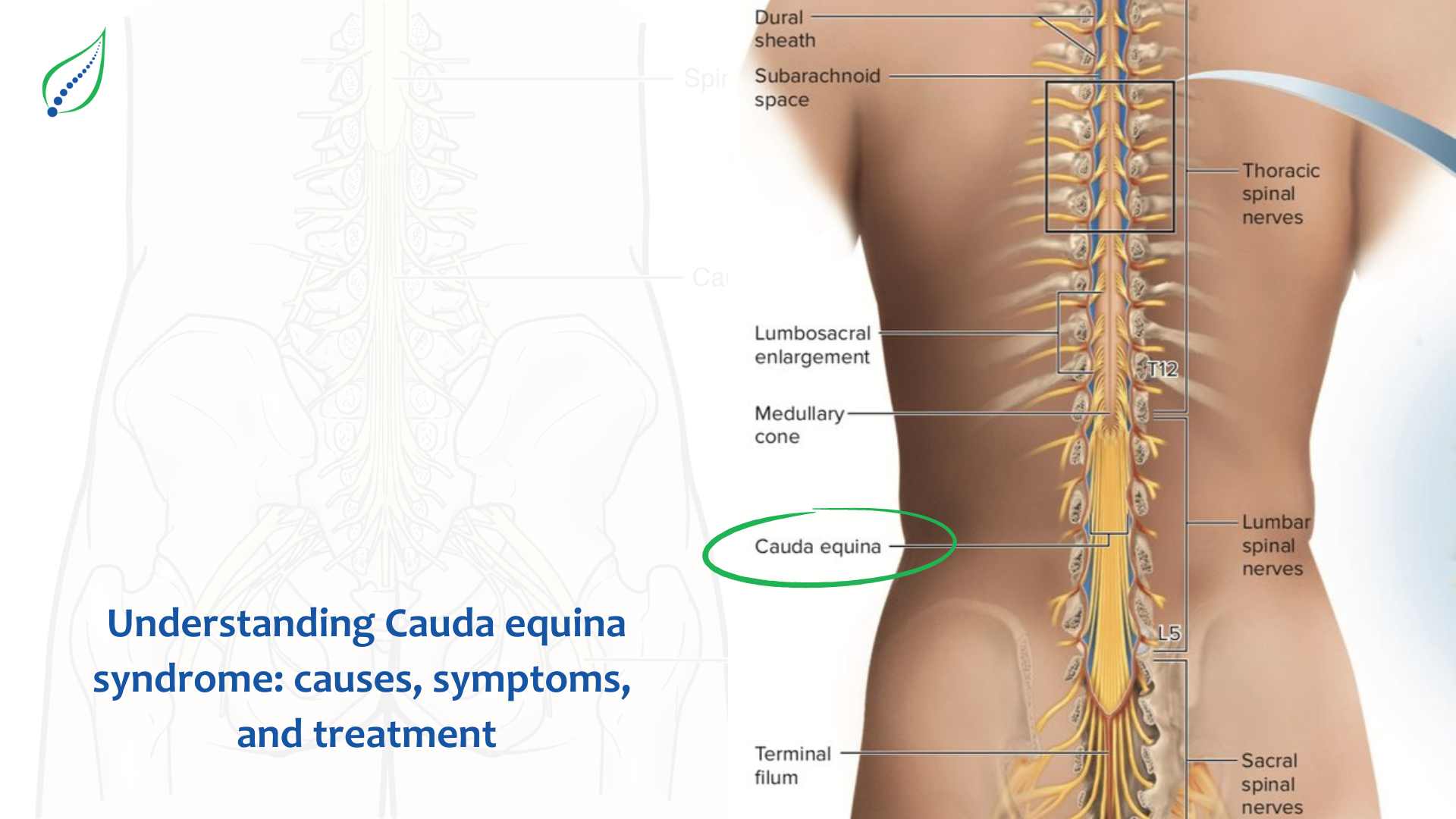
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a rare but serious neurological condition that affects the bundle of nerve roots at the lower end of the spinal cord, known as the cauda equina. These nerves are responsible for sending and receiving messages between the brain, legs, feet, and pelvic organs. When the nerve root in the cauda equina is compressed or damaged, it can lead to a range of symptoms and potential long-term complications. In this blog post, we'll discuss the causes, symptoms, and nonsurgical treatment options for cauda equina syndrome to help you better understand this condition.
What is Cauda Equina Syndrome?
Cauda equina syndrome occurs when the nerve roots in the lumbar spine (lower back) become compressed, causing a variety of neurological symptoms. The term "cauda equina" is derived from Latin, meaning "horse's tail," as the bundle of nerve roots resembles a horse's tail.
This condition is considered a medical emergency, as it can lead to permanent paralysis, urine and bowel incontinence, and otherserious complications if not treated promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing long-term damage and achieving the best possible outcome.
Causes of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Several factors can contribute to the development of cauda equina syndrome. Some of the most common causes include:
- Herniated disc: A herniated disc in the lumbar spine can put pressure on the cauda equina, leading to compression and damage.
- Spinal stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal, known as spinal stenosis, can cause compression of the nerve roots in the cauda equina.
- Spinal tumors: Tumors, whether benign or malignant, can grow in the spinal canal and compress the cauda equina.
- Spinal infections: Infections in the spine, such as epidural abscesses, can cause inflammation and pressure on the nerve roots.
- Trauma: Injuries to the lower back, such as fractures or dislocations, can damage the cauda equina.
- Inflammatory conditions: Certain inflammatory conditions, such as ankylosing spondylitis or Paget's disease, can lead to cauda equina compression.
Symptoms of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome can present with a variety of symptoms, depending on the severity and location of the compression. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Severe low back pain: Pain in the lowerback that may radiate to the legs, buttocks, or perineal area.
- Sciatica: Pain, numbness, or weakness in one or both legs due to compression of the sciatic nerve.
- Saddle anaesthesia: Loss of sensation in the area of inner thighs, buttocks, and perineal area.
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction: Difficultycontrolling bowel movements or urination, or incontinence.
- Sexual dysfunction: Loss of sensation or function in the genital area.
- Weakness or paralysis: Weakness or inability to move the legs or feet.
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially in combination, it's essential to seek immediate medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent permanent damage and improve your chances of a full recovery.
Nonsurgical Treatment Options for Cauda Equina Syndrome
It's important to note that nonsurgical treatments may not be appropriate for all cases of cauda equina syndrome, particularly those involving severe compression or neurological deficits. Surgery is necessary to decompress the nerve roots and prevent permanent damage. In many cases of cauda equina, it is necessary to closely monitor patient for clinical symptoms and investigations. Those who are not medically fit or ready for surgery following treatment options can be explored.
These include:
- Physical therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches can help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. A physical therapist can design a customized rehabilitation program based on your specific needs and goals.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, prescription pain medications may be necessary.
- Epidural steroid injections: Injections of corticosteroids into the epidural space around the spinal cord can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can help manage cauda equina syndrome. Your healthcare provider may also recommend modifications to your work or home environment to reduce strain on your back.
- Bracing: In some cases, a back brace or lumbar support may be recommended to stabilize the spine and alleviate pressure on the cauda equina.
Bottom Line
Cauda equina syndrome is a serious neurological condition that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition, you can be better prepared to recognize the signs and seek appropriate care.
_1744793045.png)
_1743751136.png)
_1738219992.png)
