Thoracic Spondylosis: Symptoms, Cause, and Treatment
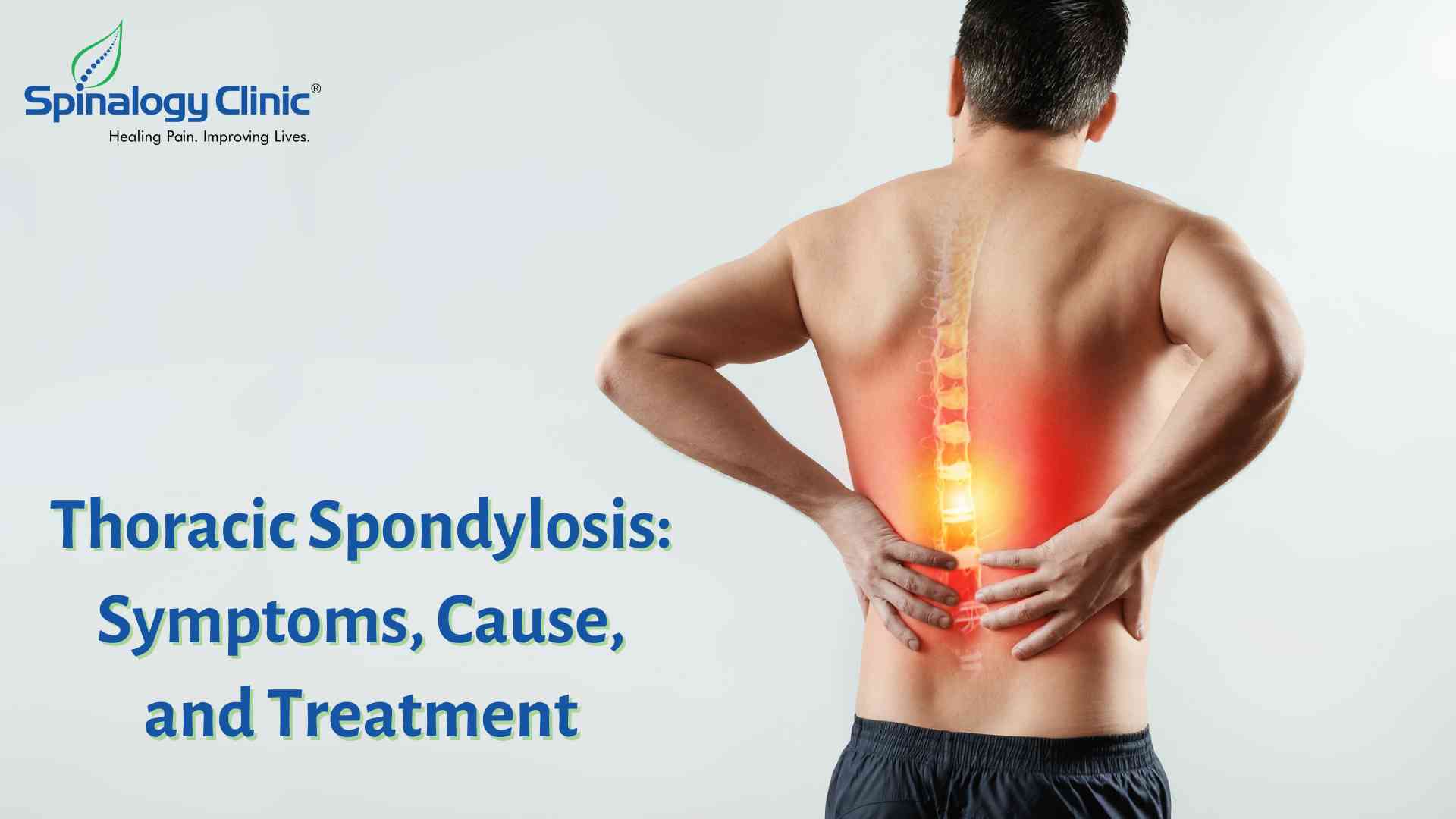
Thoracic Spondylosis is a painful degenerative spinal condition. The condition is caused by a wear and tear on the spinal discs and joints. These changes in back may cause extreme discomfort even while performing simple movements. The changes you experience in your life as you age affect your body. Spondylosis is a progressive degenerative condition of the Spinal column that affects more than 85% of people over the age of 60. Spondylosis can be of cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine. If Thoracic Spondylosis is left untreated, the symptoms will have a negative affect on the quality of life.
What is Thoracic Spondylosis?
Degenerative changes of the spine include thoracic spondylosis, spinal osteoarthritis, and degenerative disc disease. The middle of your back is the thoracic region of your spine. There are two additional segments on the top and bottom of the thoracic portion of your spine. The upper segment of the spine, which includes the neck, is known as the cervical region. Your lower back is the lumbar region.
Spondylosis can affect any area. Less frequently occurring than lumbar or cervical spondylosis is thoracic spondylosis.
Cause of Thoracic Spondylosis-
Wear and tear on the vertebrae and the shock-absorbing discs between each vertebral bone results in thoracic spondylosis. Age-related disc degeneration and the accumulation of excess bone (osteophytes) around the vertebrae might irritate some spine structures. Over the age of seventy or if the spine has previously been injured, thoracic spondylosis is more prevalent.
Thoracic spondylosis typically appears after cervical or lumbar spondylosis, as you place less stress on your thoracic spine than the other back regions. Your spine is more susceptible to difficulties when one area of your back is troubled.
The daily strain on the spine for older people increases over time. Heavy lifting and an active lifestyle may be the root of spondylosis. Stress fractures in the vertebrae may be exacerbated by osteoporosis; a bone-weakening disorder which decreases bone density and is also linked to ageing.
Symptoms of Thoracic Spondylosis-
The mid back frequently feels stiff, especially when turning around and reaching for objects. These motions might hurt you as well. Pain in the mid back and upper back region may worsen in lying flat on the back and in prolonged sitting. If a nerve is pinched or irritated, you could have neurological symptoms like weakness and tingling in your, back, chest or stomach. You might feel less strong in these areas and need help to perform your usual daily tasks.
Other symptoms are-
- Spasm
- Mid back clicking
- Mid back locking
- Cramps
Investigations:
Your doctor will likely order X-rays in addition to obtaining your medical history and present symptoms if spondylosis is suspected. An X-ray will often reveal some spondylosis symptoms in most persons over 60. Bone fractures can be identified and diagnosed using X-rays.
An MRI scan shows the nerves and soft tissue surrounding the spine in great detail. An MRI can frequently determine the cause of a pinched nerve if your doctor suspects one.
Treatment for Thoracic Spondylosis-
Usually, Non-surgical multidisciplinary treatments give pain relief from thoracic spondylosis.
You can treat this condition non-surgically by using the following methods:
1. Medications:
use of medications can reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
A pain reliever, a muscle relaxant, or anti-inflammatory medication may be prescribed in more severe cases.
2. Physical therapy:
- Physical therapists can design exercise programs that improve posture, strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, and increase flexibility.
- Pain can be relieved and mobility can be improved by manual therapies such as myofascial releases and joint mobilization.
3. Heat and cold therapy:
A heat pack or cold pack can be applied to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. If you want to achieve the best results, alternate between heat and cold therapy.
4. Changes in lifestyle:
- Make sure you maintain a healthy weight in order to reduce spinal stress.
- Take good care of your posture, especially if you spend a lot of time sitting.
- Don't lift heavy objects or engage in activities that put too much strain on your spine.
Summary-
Even if you don't experience symptoms of thoracic spondylosis, exercise is still necessary to maintain your flexibility, develop your core muscles, and maintain your spine healthy.
_1744793045.png)
_1743751136.png)
_1738219992.png)
