Understanding Spine Compression Fractures and Their Treatment
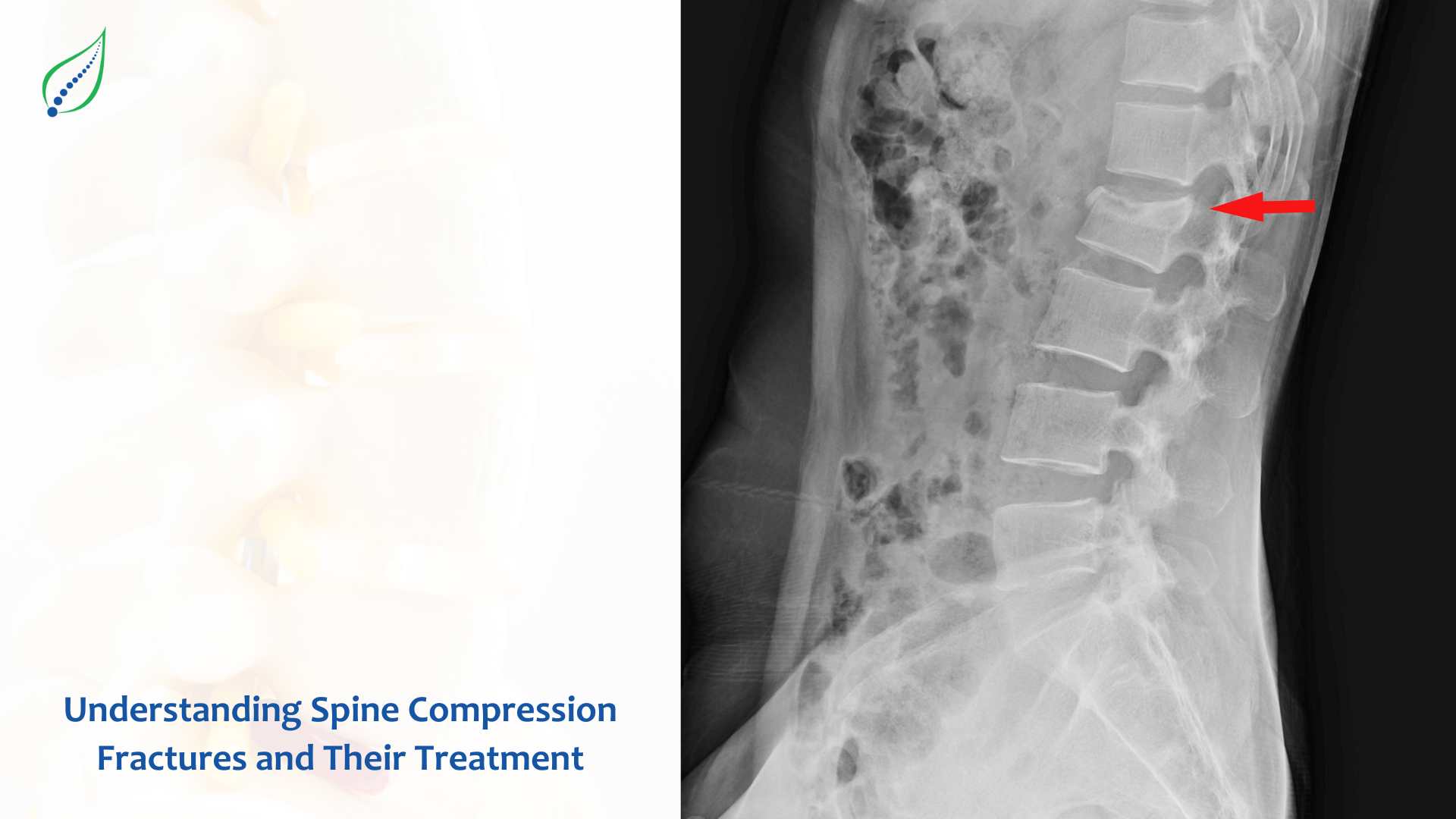
Fractures caused by spine compression are a frequent but frequently unnoticed problem that greatly affects life's enjoyment. These fractures, happening in the backbone's vertebrae, can cause pain, restricted movement and sometimes changes of form in your body. A compression fracture is when one of the vertebrae, which makes up your spinal column or backbone, breaks or cracks.
Usually, these breaks occur in the vertebral body. This is a thick and round part at front of every vertebra. When one vertebra breaks, it may collapse causing the spine to become weaker and possibly resulting in gradual changes of posture over time. Compression fractures can take place anywhere along your spine but are usually seen in the thoracic area that is middle part of your back.
Types of Compression Fractures
Compression fractures can be categorized into three primary types. The initial one is known as a wedge fracture, which occurs when the front part of a vertebra collapses and forms an angled shape resembling that of a wedge. Second type refers to crush fracture where whole vertebra undergoes impact resulting in its compression on itself.
Thirdly we have burst fractures - this form is more extreme and happens when the vertebra breaks not just in one direction but multiple directions, potentially causing issues with nerves or tissues close by. For each category, there are variations in the seriousness and effect on overall spinal health for patients.
Causes and Risk Factors
Compression fractures, caused by forceful injury to the spine like in car accidents or falls from high places, are most frequently brought on by osteoporosis. Osteoporosis weakens bones over a period of time and makes them prone to breaks.
Compression fractures are common in age 50 years or more, being female, especially after menopause, earlier history of compression fractures, circumstances that impact bone strength and cancer that has spread into the spine. Knowing these risk factors may help people take actions to prevent such fractures and get treatment sooner if needed.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of a compression fracture can be very different, ranging from weak to strong. For some people, they may not even understand that they have a fracture while others might feel severe pain. Typical symptoms include sudden start of back pain, increased pain during movement which reduces when resting, restricted mobility and flexibility, tingling or numb feeling in the back area, weak muscles or spasms and gradual loss of height.
A strong signal of having multiple compression fractures is a clear shift in posture, frequently causing the person to look hunched-over, which is called kyphosis. Recognizing these symptoms may result in quicker identification and better treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If there is a thought that you might have compression fracture, it becomes very important to go and get medical help. Usually, your healthcare provider will do physical examination on you and ask for imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans or MRIs in order to make sure of the diagnosis and also check how bad the fracture is.
Compression fractures treatment has goals to decrease pain, make spine steady and stop potential fractures. The method used can change based on what caused the fracture and how serious it is but typical treatments comprise of conservative management, medications for bone health as well as less intrusive procedures.
Conservative Management and Medications
In numerous compression fractures, particularly those caused by osteoporosis, less extreme methods of treatment are usually enough. These can involve medication for pain like non-prescription NSAIDs or prescribed drugs, wearing a brace to give the spine support and restrict movement while it heals, physical therapy for making the muscles around your back stronger, along with some rest and modifying your activities. In case of osteoporotic compression fractures, doctor may advise of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.
The usage of these methods together could greatly enhance results for patients and their life quality.
Prevention and Long-Term Outlook
Preventing compression fractures is very important, particularly when you have a high chance because of osteoporosis. Those who are likely to experience compression fractures should focus on these important prevention measures: maintaining a good diet with enough calcium and vitamin D; doing regular exercises that bear weight in order to make the bones stronger; not smoking as nicotine can make the bones weaker; taking medicines for osteoporosis exactly as per prescription and ensuring your home is fall-proofed to avoid accidents.
The future for people having compression fractures is not the same for everyone. It depends on how serious the fracture is, their general health and how well they stick with treatment. Most individuals find that their pain decreases notably within few weeks to months of receiving correct treatment. Yet it's crucial to keep in touch with your health care provider so as to control any hidden conditions and avoid more fractures from happening later on.
Bottom Line
Fractures in the spine from compression are usual and could be severe, especially for elderly people and individuals with osteoporosis. If you know the reasons, signs, and remedies available for these fractures, it can help to prevent damage to your backbone. When you have abrupt back pain or observe alterations in how you stand up straight-up, it's necessary that a healthcare professional examines this situation. By taking care and handling correctly, we can decrease the effect of compression fractures and live a good quality life.
_1744793045.png)
_1743751136.png)
_1738219992.png)
