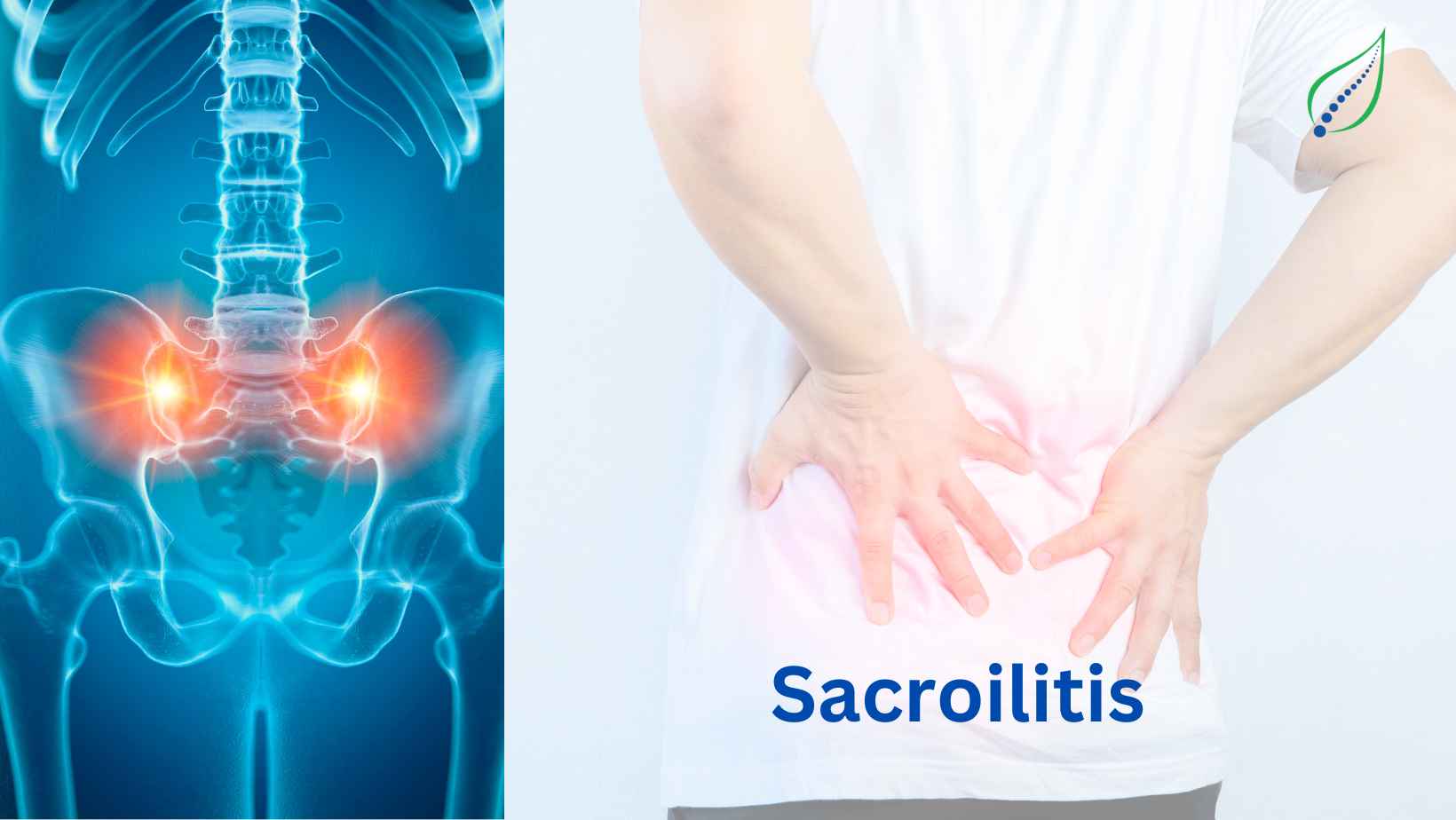
Sacroiliitis
Sacroiliitis is a condition affecting the Sacroiliac joints, in which either one or both of the joints become inflamed causing pain. The Sacroiliac joints are located on the lower part of the spine, where it connects to the pelvis. The pain is usually experienced in the lower back but can radiate to the buttocks, legs, and sometimes even feet. It has been associated with many arthritic conditions of the spine such as axil spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
Symptoms
There are certain symptoms associated with Sacroiliitis which overlap with many other disorders of the lower back making its diagnosis difficult. However, the pain due to Sacroiliitis is commonly felt in the lower back and buttocks area and might be accompanied by a fever.
- Pain in the lower back
- Pain in the buttocks
- Pain in legs and very rarely feet
The pain is usually triggered and aggravated by certain activities that put pressure on the Sacroiliac joints. Standing or running for too long, lifting heavy weights, or any activity that puts pressure on the lower back can intensify the pain.
Causes
The causes of Sacroiliitis are:
- Osteoarthritis affecting the spine
- Inflammatory arthritis such as Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Traumatic injury to the spine due to an accident such as car crash or fall
- Pregnancy can cause inflammation of the Sacroiliac joints by putting excessive weight on them due to change in the manner of walking.
- Pre-existing issues of the spine
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this condition is a bit difficult due to its similarity and overlapping with other spinal disabilities. Your physician will conduct a physical exam and, move your legs or press certain parts of your back or buttocks to check for pain in the Sacroiliac joints. A diagnostic injection might also be used to confirm the condition.
Other than these your doctor will also recommend imaging tests that are comparatively more reliable. An X-ray can help in diagnosing whether the pain is due to the Sacroiliac joints or some other condition. It will also reveal any injury or inflammation of these joints. MRI is another imaging test and is more advanced than X-ray as it provides a more detailed image.
Treatment
This condition is mostly cured with rest and physical therapy, and in more severe cases injections are needed.
Your doctor will inject therapeutic steroid injection in combination with a local anesthetic in the joints to induce recovery.
In some cases, if pain persists after conservative management, then Radiofrequency neurotomy can be performed. It is done to inhibit or disrupt the pain signals traveling along the nerve to the SI Joint.
While the treatment also involves taking over-the-counter medications along with physical therapy and proper rest, pregnant women and patients with multiple disabilities should take extra precautions. NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, TNF inhibitors are also effective for treating pain.
Non-surgical treatments for this condition also include using cold and hot pack to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation, stretching, strengthening and flexibility building exercises. These exercises will help in slowly improving the health of the joint but proper precautions should also be taken. Overdoing or putting excessive pressure on the lower back can aggravate the condition further and delay the recovery process. Along with above exercises Lifestyle changes are important to have much sustained pain free life.
_1747226427_1751827070.png)
_1744793045_1751827442.png)
_1743751136_1751830603.png)
