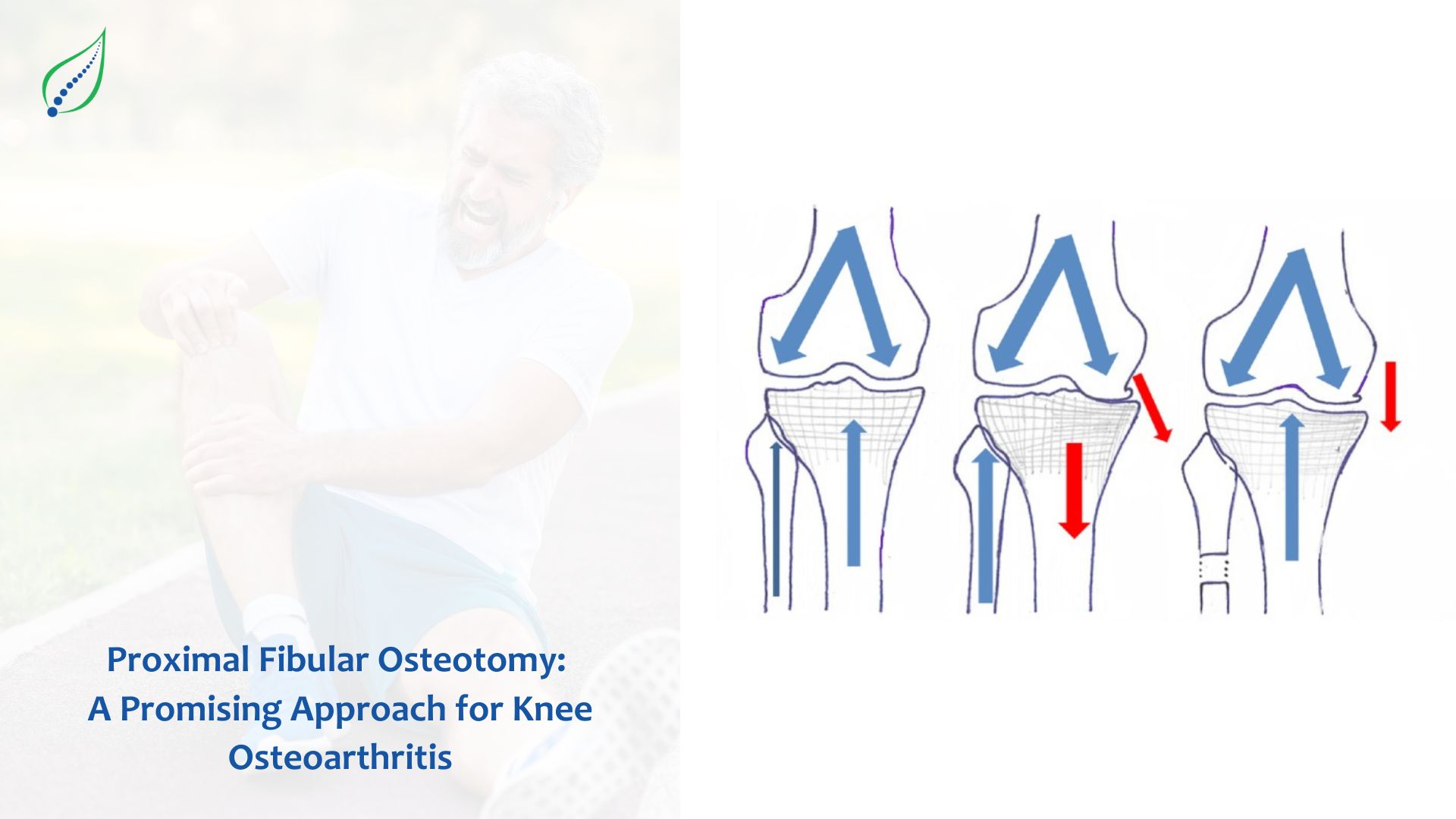
Rheumatoid Arthritis
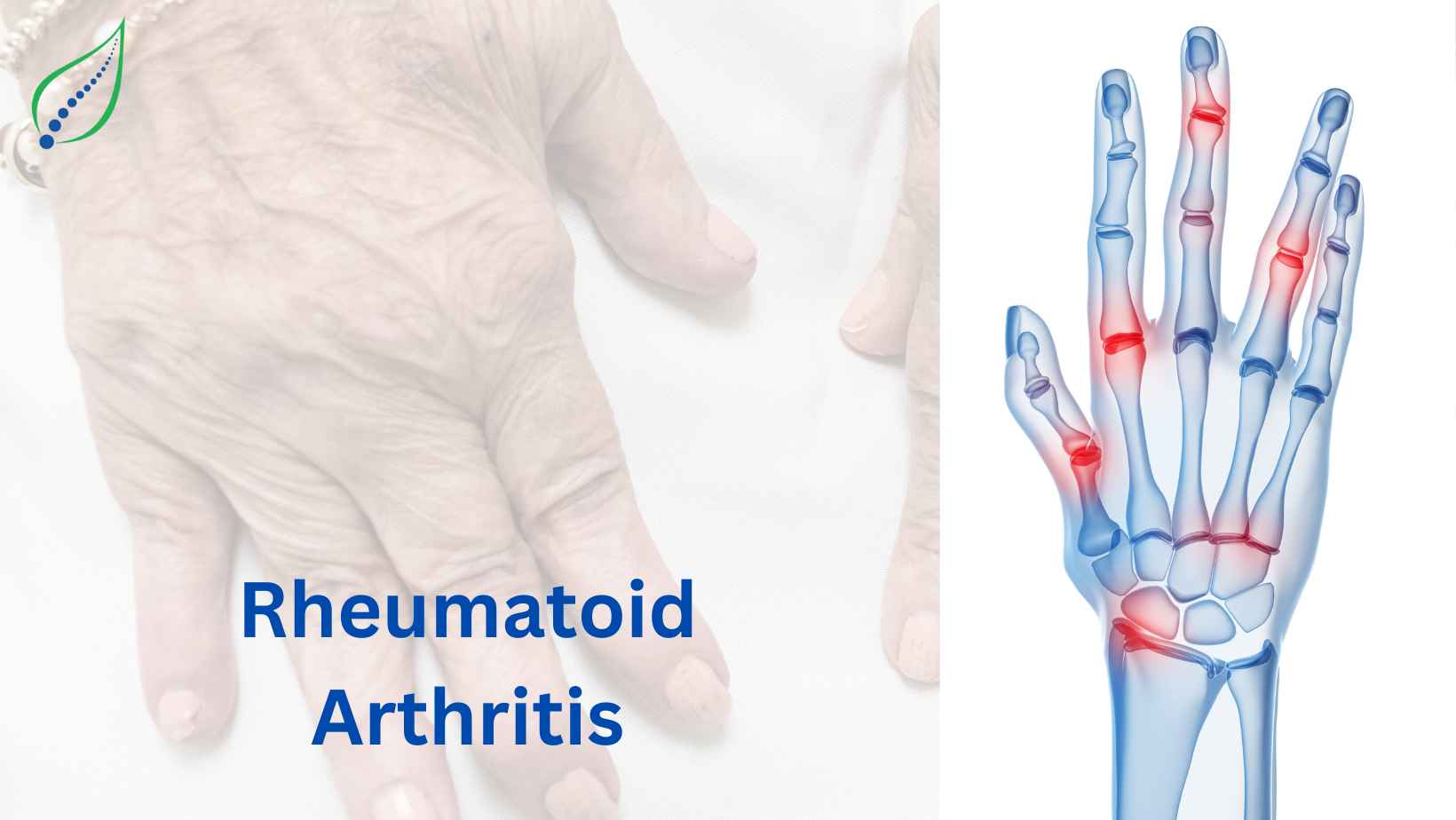
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a progressive autoimmune disease that causes pain, inflammation, and swelling, in and around the joints. The disease causes chronic inflammation and can lead to permanent deformity.
RA usually affects in a symmetrical pattern and involves the same joints on both sides of the body. It starts from the hands and feet but can attack any joint of the body.
Its most common symptoms include stiff joints, fatigue, and weakness, which is mostly experienced in the morning or after sitting for too long.
An autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s healthy tissues are attacked by the immune system. While classic RA features are joint tissue inflammation and inflammatory arthritis, the disease can also cause injury in other organs. It affects multiple organs such as joints, eyes, lungs, and even heart.
Symptoms
- Pain and Stiffness in Joints
- Warm, Tender and Swollen joints
- Deformed joints
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Impaired mobility
- Weight loss
- Weakness
This disease is chronic in nature and symptoms appear and disappear according to the severity of the tissue inflammation.
Causes
The immune system is designed to attack any invaders of the body but sometimes it malfunctions resulting in the destruction of healthy body tissues. Some people are more genetically inclined towards developing autoimmune illnesses and some studies even show that bacteria or virus triggers RA in these genetically prone people.
The antibodies of the immune system attack the smooth lining of the joints, known as the synovium. This results in inflammation and pain.
With time, inflammation causes the thickening of synovium, which over time destroys the cartilage.
Eventually, if left untreated, the ligaments and tendons are also destroying. This leads to weakening and in severe cases permanent deformation of joints.
Risk Factors
Certain people are more prone to RA than others, such as:
- Females
- Obese People
- People with a genetic background
- Active or Passive Smokers
Complications
Those who suffer from RA are also prone to some other conditions such as
- Cardiac issues
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Depression, Anxiety, and Stress
- Obesity
RA decreases mobility and can interfere with the daily lifestyle of a person. It can hamper with the mundane tasks as its flare-ups are very unpredictable.
Certain other conditions are also related to RA which can eventually develop:
- Carpel Tunnel Syndrome: This is a kind of nerve damage that occurs due to irritation of a nerve in the wrist area. Symptoms include pain, tingling, and numbness in fingers, hand, and thumb.
- Cervical Myelopathy: If joints in the neck or cervical spine are dislocated it can lead to more pressure on the spinal cord. This can lead to loss of mobility and severe pain.
- Vasculitis: Inflammation of the blood vessels can lead to their weakening, narrowing, and scarring, which can further impair the blood flow to organs, affecting their functioning.
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment are very crucial in the treatment of RA. An effective treatment strategy should be employed as early as possible to slow the progression of this disease. Early symptoms which the doctor will take into consideration while diagnosing RA are swelling, deformity, or any signs of inflammation. They may also recommend some tests.
Treatment
A rheumatologist is a specialist of the RA who undertakes the task of treating patients with RA.
Treatment can help in easing symptoms such as:
- Reduce inflammation
- Reduce pain
- Prevent the loss of functioning of the joints
- Slow down the progression of RA
- Treat the damaged joint or tendons and deformities if any.
Medications
Following medications can help in relieving the symptoms:
1.) Corticosteroids: Although steroids can reduce inflammation, when sudden flare-ups happen, doctors can inject steroid injections to provide rapid relief. However, the duration of its effect depends upon the severity of the flare-up. Long-term use of steroids can have many side-effects such as cataracts, osteoporosis, glaucoma, diabetes, etc.
2.) NSAID’s (Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs): These are over-the-counter drugs which can ease symptoms for some time.
3.) DMARDS (Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs): These drugs are immune-suppressants that prevent the hyperactive immune system from damaging the joints. An example includes leflunomide, methotrexate, minocycline, etc.
4.) Biologicals: RA being inflammatory arthritis, there are many inflammatory mediators –cytokines – which cause the organ damages as well as patient symptoms of inflammation. Biologics are similar to the substances that block these mediators from causing inflammation. Biologics which are used for RA are genetically engineered from living cells. These are used when DMARDs are not effective and can be used in combination with DMARDs as well. Commonly used biologics for RA are Tocilizumab, Etanercept, Adalimumab, Infliximab, etc.
All the drugs are strict to be taken under Doctor’s observation and patient needs to be monitored for side effects.
5.) Physiotherapy: Very useful to keep joints mobile and reduce inflammation. Sued in painful and stiff joints to keep them pain-free and mobile.
6.) Intra-articular Injections: Sometimes intra-articular steroid injections are used to treat acute inflammation. These shall be used with precautions because if used too many times, they can aggravate the damage to the cartilage.
Prevention
Although it is mostly dependent on genetics one can always take good care of health as a precautionary measure. Avoiding smoking and maintain healthy body weight is crucial in avoiding health issues. If there are any symptoms, seek treatment as early as possible to obtain the best results.