Reactive Arthritis
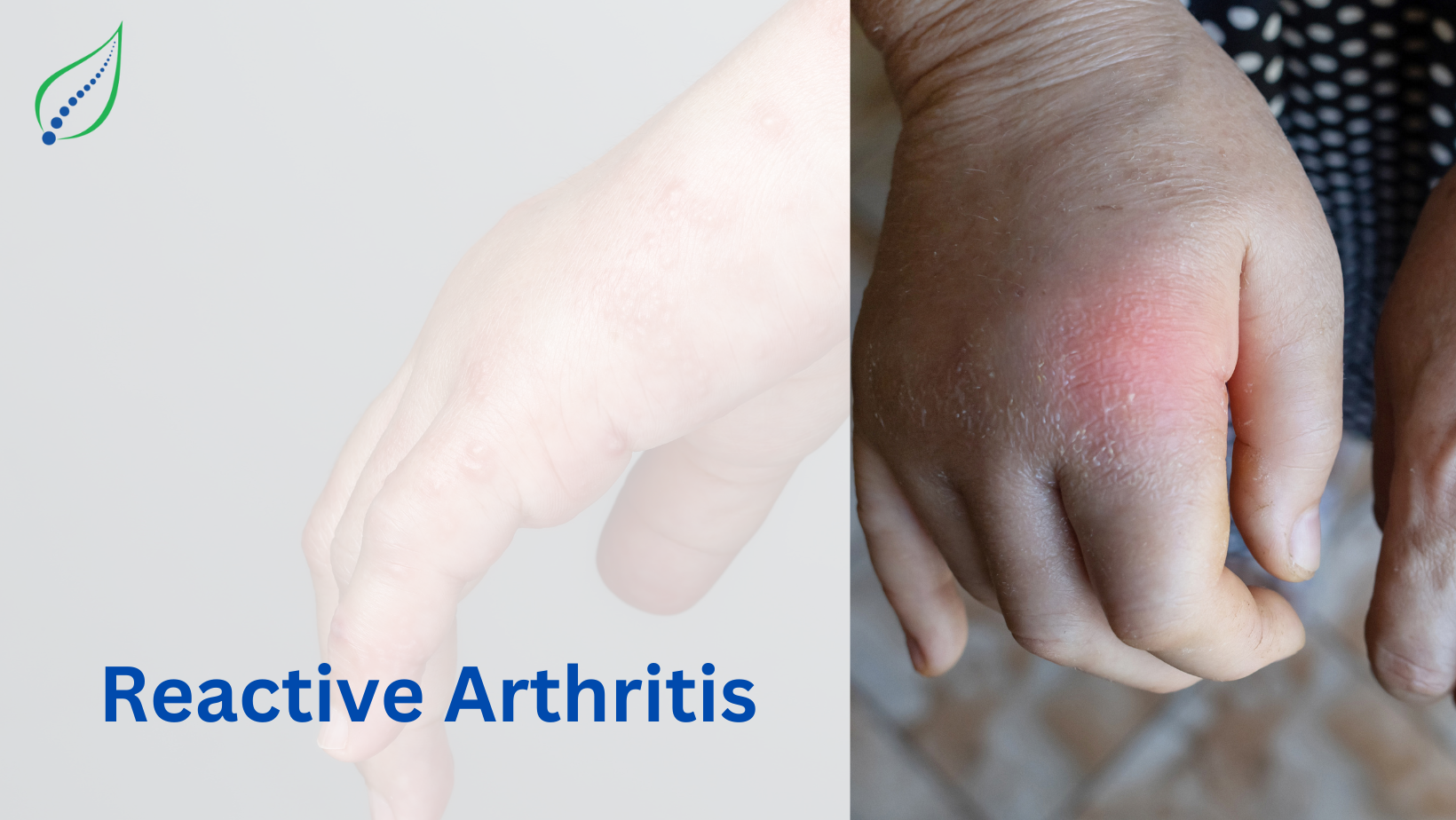
Reiter’s syndrome or reactive arthritis is an inflammatory arthritis that manifests several days to weeks after a gastrointestinal or genitourinary infection. Inflammation of the joints, eyes, and urinary tract are hallmarks of reactive arthritis. Triad includes arthritis, urethritis, conjunctivitis.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
It is an immune-mediated syndrome triggered by an infection. It is hypothesized that T lymphocytes are induced by invasive bacterial fragments that reach the systemic circulation. These activated cytotoxic-T cells then attack the synovium and other self-antigens through molecular mimicry. It is believed that anti-bacterial cytokine response is also impaired in reactive arthritis, resulting in the decreased elimination of the bacteria.
SYMPTOMS:
Some people with reactive arthritis have mild symptoms, while others have severe symptoms that limit daily activities. The symptoms typically start 1 to 6 weeks after an infection of the digestive or urinary tract or genitals, but the infection has usually resolved by the time symptoms arise. The onset is typically fairly sudden, usually over the course of a few days.
Reactive arthritis is characterized by inflammation of the joints, eyes, and urinary tract, but not everyone with the condition will experience all three, or they might not occur at the same time. The main symptoms are:
Joint pain and stiffness:
Joints may become painful, red, and swollen, especially the large joints of the lower limbs, such as the knees and ankles.
Morning stiffness or night pain is typical. The affected joints are usually on one side of the body.
Pain in the heel or foot is a sign of inflammation.
- Inflammation of the urinary tract: Increased urinary frequency and burning while urinating.
- Eye inflammation: Conjunctivitis, can cause redness, pain, burning, itching, blurred vision, or sensitivity to light.
- Other symptoms include- Fatigue, Fever, Weight Loss, Diarrhoea, Skin rashes, Ulcers in mouth.
- For sexually acquired reactive arthritis, there is a history of sexual intercourse, usually with a new partner, within 3 months of arthritis symptoms. Genital symptoms precede arthritis by about 2 weeks on average. It may include dysuria, discharge, testicular pain in men, and intermenstrual or postcoital bleeding, or deep pelvic pain apart from vaginal discharge in women.
INVESTIGATIONS:
Doctor may suggest certain Blood tests and imaging such as XRAYs to rule out signs of reactive arthritis.
TREATMENT:
The goal of treatment is to manage your symptoms and treat an infection that could still be present.
Medications:
- Antibiotics if, arthritis was triggered by a bacterial infection.
- NSAIDs can relieve the inflammation and pain of reactive arthritis.
- A steroid injection into affected joints can reduce inflammation and allow you to return to your usual activity level. Steroid eye drops may be used for eye symptoms, and steroid creams might be used for skin rashes.
- Rheumatoid arthritis drugs can relieve pain and stiffness for some people with reactive arthritis.
Physical Therapy : Exercise to stretch & strengthen your joints & muscles. Maintain joint ROM to increase joint flexibility & reduce joint stiffness.