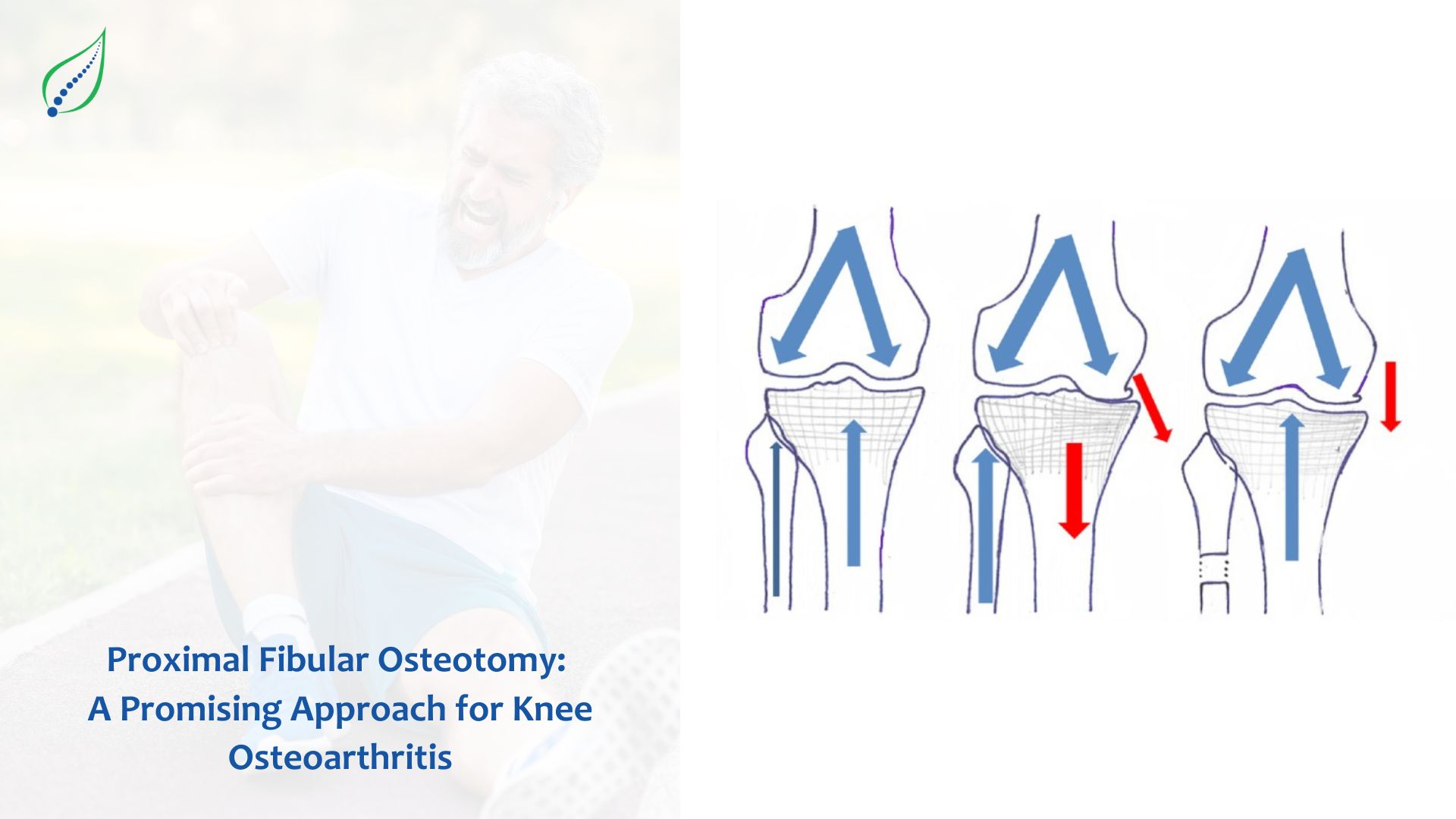
Ischial Tuberosity Bursitis
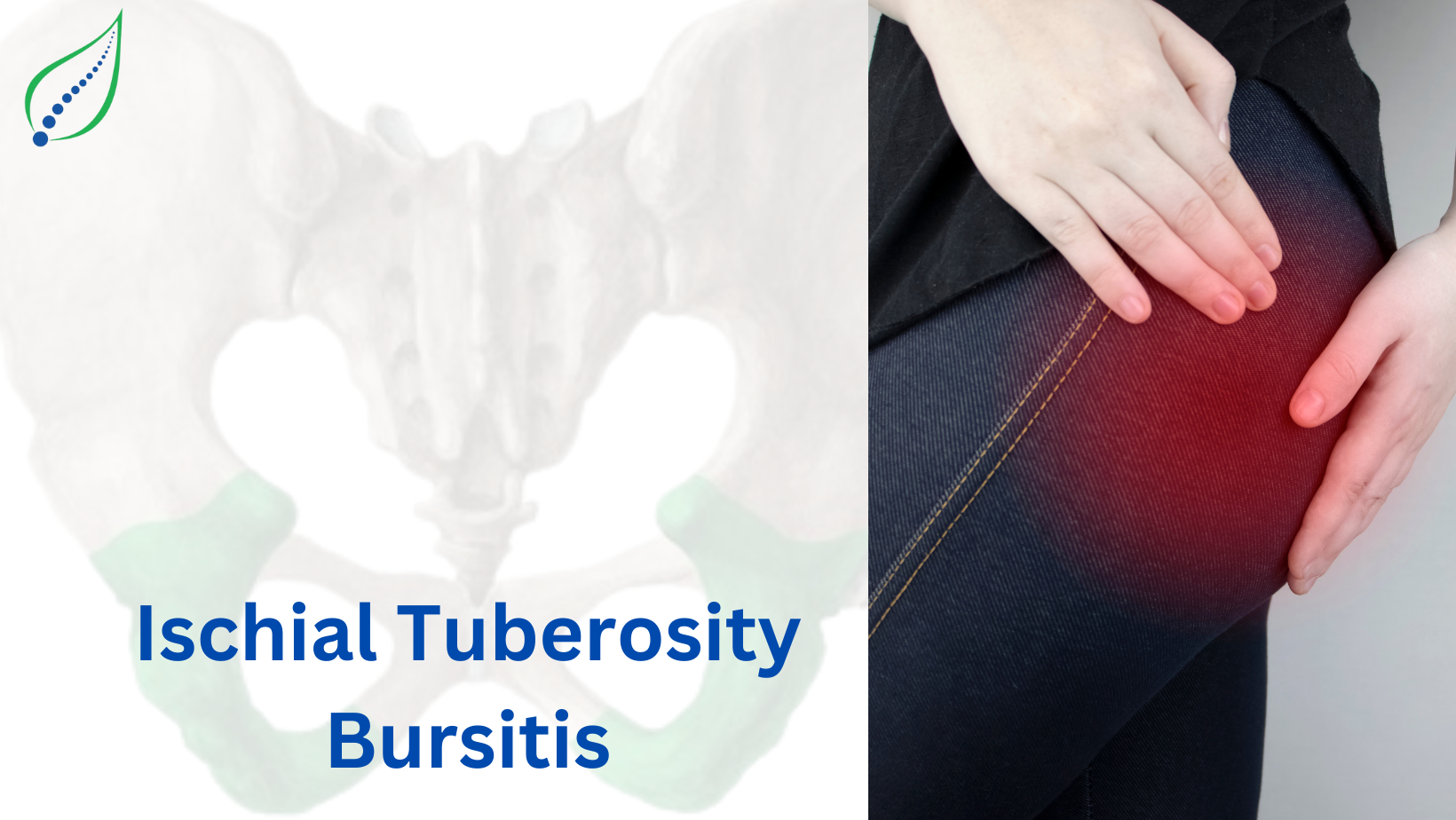
Sitting bone pain can be diagnosed as ischial bursitis. Bursa is a fluid-filled sac located between ischial tuberosity and the tendons that connect the hamstring muscle. An inflammation in this area is called ischial bursitis.
The ischial tuberosity is a rounded bone that extends from the ischium. It is located just below the ischial spine. Three tendons connect the hamstring, a muscle in the back of your thigh, to the ischial tuberosity.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
The ischial bursa is composed of a fatty connective tissue capsule filled with synovial fluid. An infection or irritation occurs, cells of synovia proliferate, resulting in increased production of synovial fluid. It is most common in persons with sedentary careers with constant irritation of the ischial bursa due to prolonged periods sitting on hard surfaces.
Other causes include:
- Repetitive activities
- Gout
- Pseudo gout
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Trauma
- Skin infections
SYMPTOMS :
Most common symptom is a deep aching pain in the region of the ischiogluteal bursa.
- Pain worsens when you sit.
- Increased pain while sleeping on the affected side.
- Redness or swelling around the bursa on the site of pain.
- Tenderness in the upper and lower thighs and buttocks.
- Inflammation of the lower buttocks and hips.
- Inability to fully extend the hip.
- Radiating pain from the buttock down the leg.
- Sleeping problems due to hip discomfort.
- Aching or stiffness in your pelvis.
INVESTIGATION:
Blood reports should be necessary if an infection or autoimmune condition is suspected.
Ultrasonography
MRI test is only necessary if their other possible differentials, such as tumors, abnormal increased fluid intensity signals in ischial bursae on both sides.
Physical Examination: On palpation, a small, smooth, no mobile mass may be felt overlying the ischial tuberosity. Tenderness over the buttock.
Straight leg raise and FABER test may elicit pain.
TREATMENT:
The treatment for this entity includes analgesics, cold therapy, rest, fractional massage and therapeutic stretch exercises
- Medications- NSAIDS, Analgesics
- Rest & icing- Stop the activity that caused the bursitis whether it was a physical activity or sitting for long periods on hard surfaces. Apply ice packs at the painful site for 10 mins, 3-4x/day
- Injections- local steroid injections to reduced inflammation
- Regain range of motion
- Improve strength and coordination
- Reduce friction on the bursa
- A physical therapy for ischial tuberosity bursitis normally lasts for 4 to 6 weeks. These treatments to relieve pain & restore strength to hamstring & surrounding muscles.