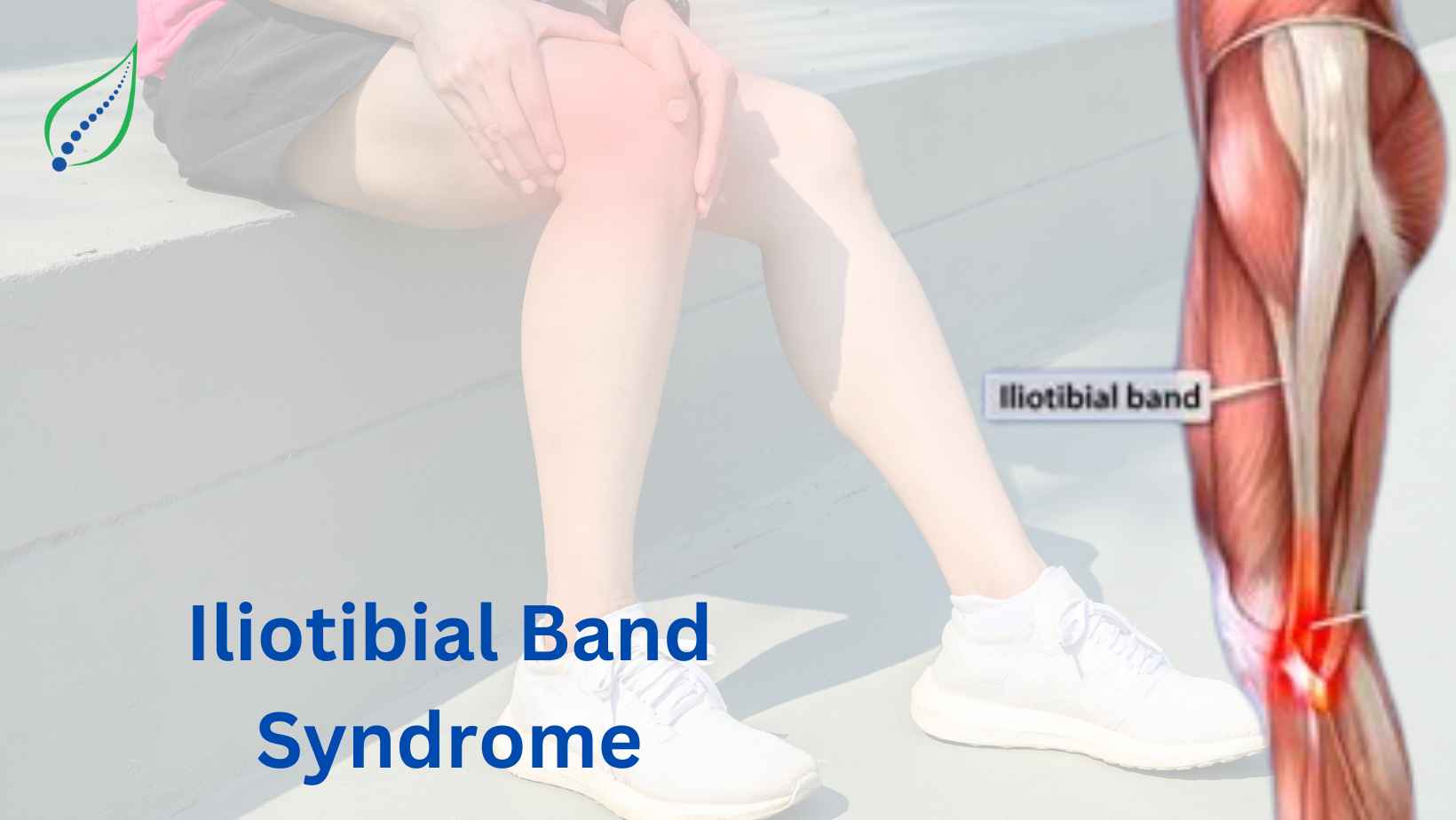
Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome is caused by running, hiking, cycling, and activities that require bending the knee in general. The pain is experienced in the outer part of the knee and is a result of the injury of the IT Band, a connective tissue that runs from the outside of the hips, thighs, and crossing the knee joints. Inflammation of the IT Band is very common as it moves backs and forth while walking, running or any other activity involving the knees.
Causes of Iliotibial Band Syndrome
The cause behind the swelling and inflammation of the IT Band is friction. It moves back and forth as the knee extends and sometimes it can tighten up. Bursa which is a sac filled with fluid helps in the smooth gliding of the knee. But when there is an overuse or repeated strenuous movement of the knee, pain can be experienced. This can eventually damage the IT Band as well as the Bursa, decreasing the overall range of motion of the knee.
A few causes of the IT Band syndrome are:
There are multiple reasons as to why one is affected with IT Band syndrome but it most commonly happens to athletes, runners, and cyclists as they tend to use their knee joints more frequently and for long durations.
- Poor workout habits such as avoiding or not doing enough warm-up and stretching.
- Wearing the wrong shoes.
- Not taking proper rest for the body to recover.
- Bow legs, Arthritis, and other medical conditions.
- Weakness in legs, abs, and glutes.
Symptoms of the IT Band Syndrome
- Pain in the lateral or outside of the knee is the most common symptom.
- Decreased range of motion of the knee.
- Swelling and redness of the knee.
- Snapping and popping sounds when the knee is moved.
- Pain spreading to thighs and hips.
Diagnosis
This condition is usually diagnosed by studying the medical history of the patients and by doing a physical exam. Certain symptoms such as pain in the outside knee and worsening of the pain when the heel touches the ground hints at IT Band Syndrome.
The visible symptoms such as swelling and redness also help in identifying this condition. In more complicated cases where it’s not possible to easily evaluate the disorder, the doctor might suggest an X-ray or an MRI. These help in ruling out the other possible causes of knee pain.
Treatment
Rest:
Take proper rest. Take all the precautions so the injury doesn’t get worse. Do not perform activities that put stress on the knee.
Cold Fomentation:
Apply an ice-pack over the knee.
NSAID’s:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID’s) to help with pain and inflammation.
Local Steroid Injection:
Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that can be injected into the IT Band. These injections provide pain relief and reduce inflammation.
Manual Therapies:
Application of certain therapeutic modalities like ultrasound, IFT helps to reduce pain and swelling around the knee. In ITB Syndrome, Physical therapy treatment can be effective in reducing your symptoms and getting you back to performing normal activities. Physical Therapy and stretching plan to help relieve pain and strengthen the muscles.
_1749797551_1751826891.png)


