Genitofemoral Neuropathy
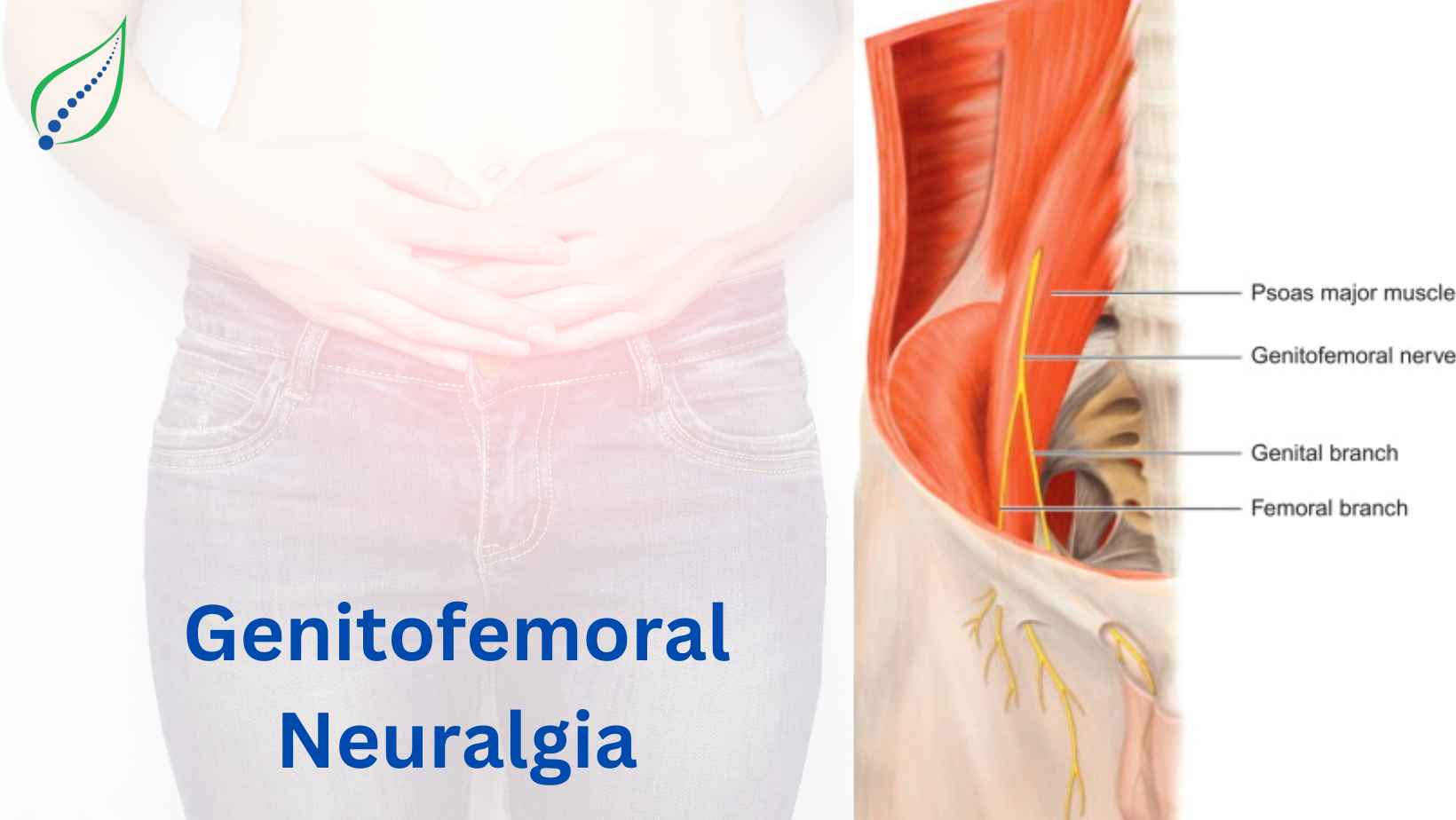
Genitofemoral neuropathy or genitofemoral neuralgia is caused along the genitofemoral nerve when it is injured or damaged. The groin is supplied by a group of nerves that control muscle function and sensation. The genitofemoral nerves arise from the spinal cord and supply the skin and structures around the groin area. The genitofemoral nerve divides into two branches, the femoral branch, and the genital branch. The femoral branch supplies sensation to the upper anterior thigh and the genital branch supplies sensation to the anterior scrotum in males and labia majora and parts of vulva females.
Genitofemoral neuralgia occurs in the pelvis area and is a very severe kind of pain. This condition usually remains undiagnosed for some time and identifying the cause of this pain can be a difficult task.
Causes
Any damage to the genitofemoral nerve can lead to this condition. The following conditions can cause genitofemoral neuralgia.
1.) Abdominal Surgeries: The genitofemoral nerve can be damaged during certain types of abdominal surgeries such as hernia repair, appendectomy, etc.
2.) Trauma to Pelvis or Abdomen: Trauma to the abdominal wall or compression of the tumor on the nerve fibers can cause this neuralgia.
3.) Compression of psoas muscles: If the psoas muscle is subjected to compression the genitofemoral nerves can get damaged.
4.) Other Causes: Other underlying causes responsible for peripheral neuropathy such as diabetes, multiple sclerosis, chronic alcoholism, chemotherapy, or even vitamin deficiencies in the body can lead to genitofemoral neuralgia.
Symptoms
This condition is similar to other nerve-injury related disorders and is characterized by an excruciating groin-pain along with the distribution of this nerve. This condition is chronic and the pain keeps returning from time to time. The pain can be felt anywhere near the abdomen and lower back.
Treatment
The diagnosis, as well as treatment of this condition, can be challenging as medications prescribed for this condition can have side-effects. Some of the treatments are Anticonvulsant Drugs, Steroids, and Nerve Blocks. In very serious cases surgical intervention is required, but surgery also poses the risk of aggravating the pain even more.
1.) Nerve Block: The most recommended treatment for genitofemoral neuralgia is differential nerve blocks. This technique differentiates the genitofemoral nerve from the overlapping ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerve.
2.) Pulsed Radiofrequency: Pulsed RF treatment usually offered only if the above treatment options fail.
3.) Topical Treatment: Topical treatments such as lidocaine patches and gabapentin can also be used.
Management
This disease can be very difficult to cope with as the pain can be confusing in the beginning. Its diagnosis is also very difficult and usually requires multiple visits to the physician for identifying the cause of this excruciating pelvic pain.
This not only leads to physical discomfort but also causes strain on mental health. Patients feel frustrated and angry due to the recurrent nature of this condition and thus maintain mental well-being is also very crucial.
There are many communities and support groups where people come together to address their problems and frustrations. These can be very helpful in finding people undergoing similar painful experiences and relieving built-up stress. A psychologist can also be very helpful in dealing with the pain by methods such as deep-breathing techniques and relaxation methods.