Chondromalacia Patellae
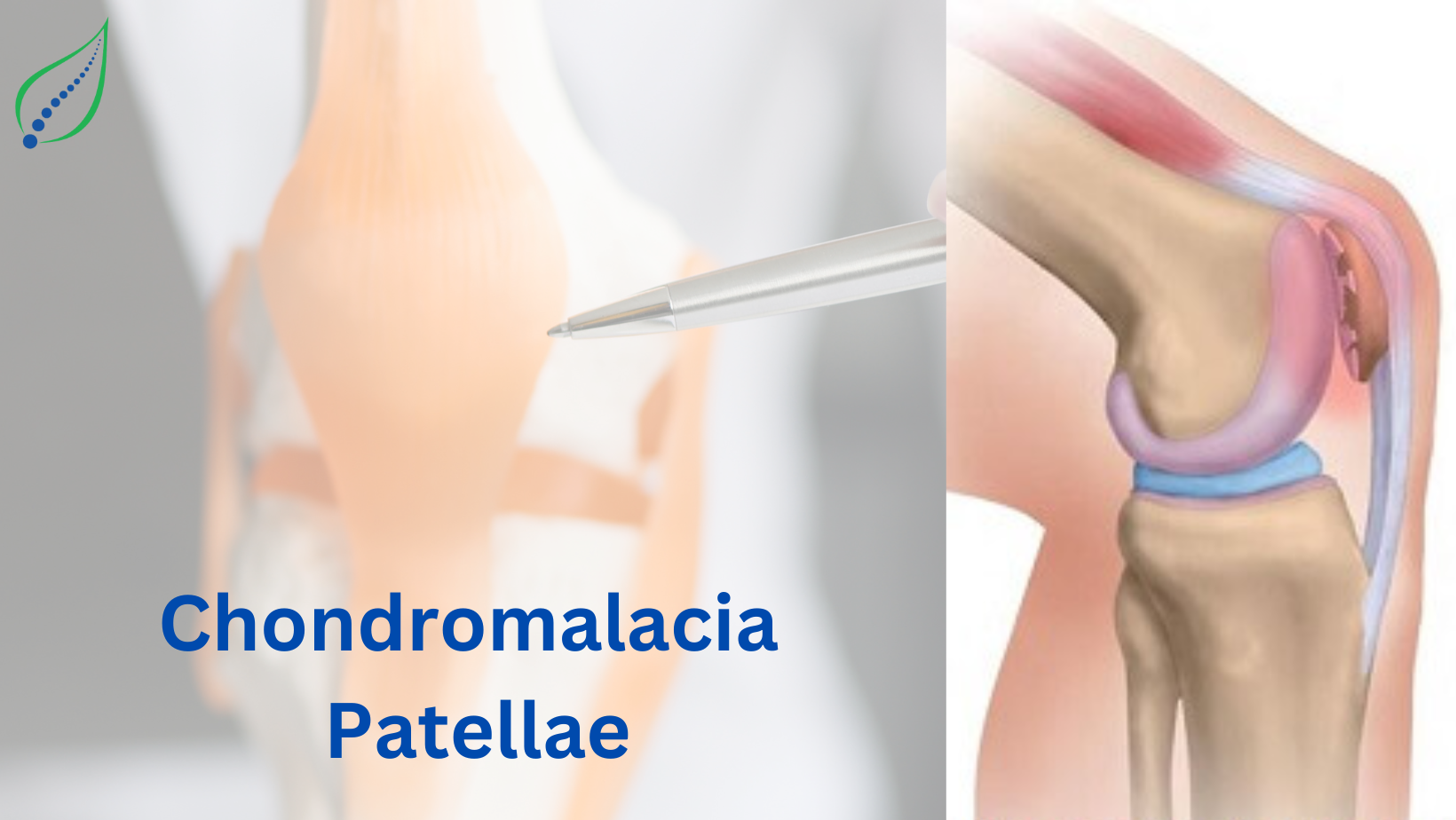
In chondromalacia, Chondrus means "cartilage" and malacia means "softening" which generally called as sick cartilage. Generally, the patella is lined by hyaline cartilage, in chondromalacia patella the posterior articular surface loses its density where healthy cartilage becomes soft in turns starts tearing, fissuring and erosion of hyaline cartilage occur. In chondromalacia patella the extensor mechanism of knee is affected. The lower surface of patella is covered with hyaline cartilage which articulates with hyaline covered femoral groove.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
Patellar hyaline cartilage has bluish -white, smooth, glistering and resilient nature. The Pathology initiates with softening, swelling, oedema of articular cartilage that gives slight yellowish-white appearance to the cartilage. The injury starts at middle of medial patellar facet or distal to it and progress into cartilage fibrillation, fissuring and fragmentation in later stages.
CAUSES:
- Muscular weakness
- Patellar lesions
Chondromalacia patella is basic mal-alignment syndrome which occurs due to:
- Increased Q-angle
- Increased Patellofemoral Dysplasia
- Femoral anteversion
- Genu valgum
- External tibial torsion
- Pronated feet
SYMPTOMS:
- Anterior knee pain
- Pain while changing position from sitting to standing
- Tenderness on palpating medial and lateral border of patella
- Crepitus on movement
- Swelling around patella or knee joint
- Weakness of Vastus medialis
- Increased Q-angle
DIAGNOSIS:
Radiographs- X-ray with AP and skyline view helps in analysing patellar positioning.
CT scan: Shows Patellofemoral alignment by delineating trochlear geometry.
MRI scan: Helps in identifying articular cartilage stages and abnormal cartilage shows High T2 signal intensity
Arthroscopy: It is efficient diagnostic modality which determines the location, size of cartilage lesion and position pf patella.
TREATMENT:
Medical management : NSAIDS are given to reduce pain and swelling.
Exercise therapy: Strengthening, Stretching and aerobic exercises helps in making joint and muscles strong. Open and closed kinetic chain exercises for hip and knee strengthening. Strengthening of core and ankle musculature to reduce stress over patella. Stretching of quadriceps, hip flexors, IT band, hamstrings, gastrocnemius and soleus.
Joint mobilization: Patellofemoral and tibiofemoral mobilization are done. Tibiofemoral mobilization is more beneficial in chronic Patellofemoral pain.
Neuromuscular training of hip abductors, extensors, knee extensors, core muscles. It will help improving kinematics and muscle activity.
Gait retraining helps in reducing stress on patellofemoral joint and to correct forward trunk lean and minimal shoes.
Taping: Medial patellar glide therapeutic taping is beneficial in mal tracking of patella.
Bracing: The braces which supports patella and reduces stress loading are beneficial.