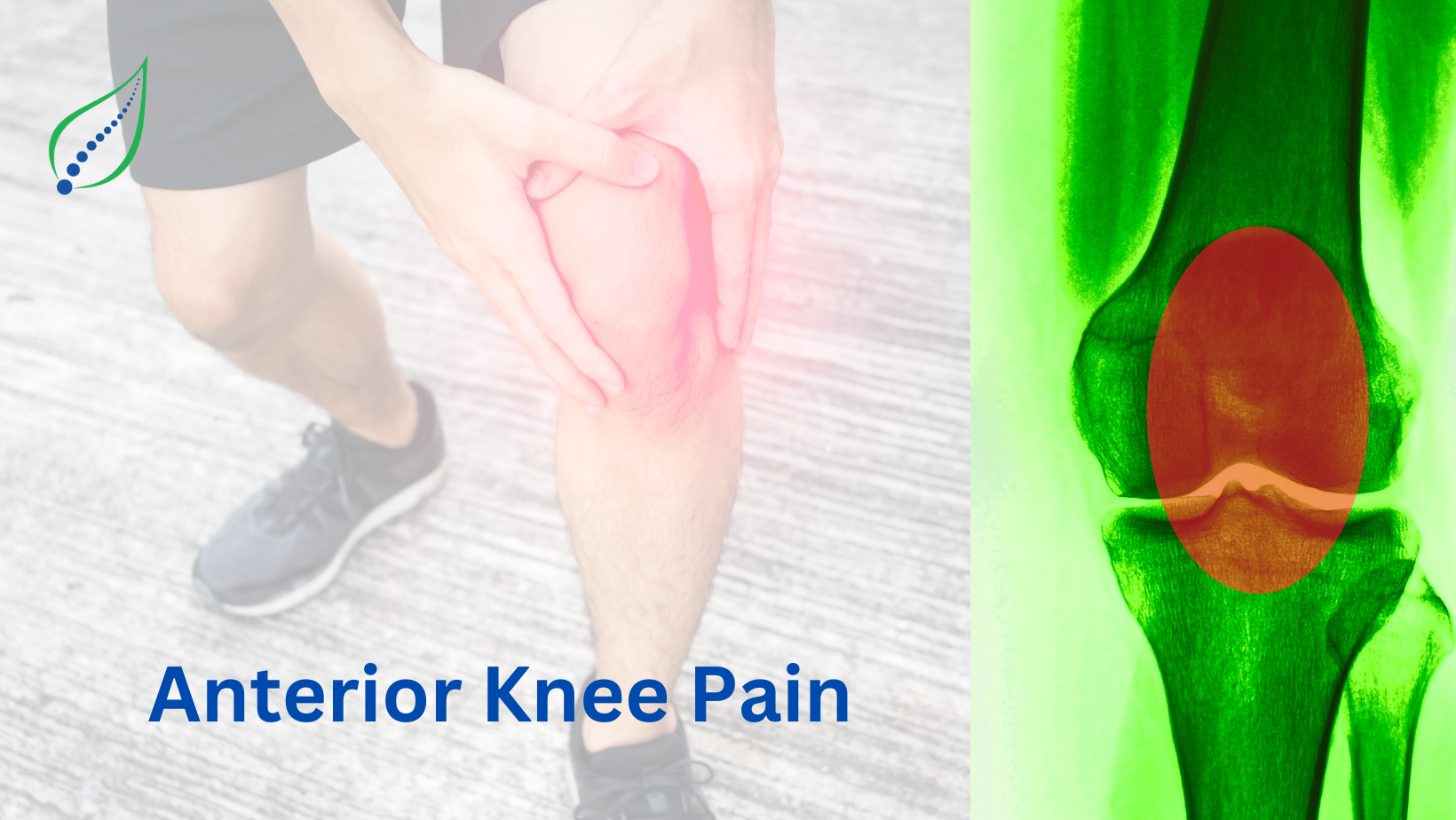
Anterior Knee Pain
Pain that occurs at front and centre of the knee is called as anterior knee pain. It can be caused by many different conditions such as patellofemoral pain syndrome, chondromalacia patellae, quadriceps tendinitis etc.
Anterior knee pain is caused by muscle- or bone-related injuries and is a dull, achy pain. Anterior knee pain is common among adolescents and adults, and can be caused by overuse, training, or structural damage. It is the most frequent reason people consult a doctor for knee conditions, and is often referred to as "patellofemoral pain".
Anterior knee pain is a range of symptoms and joint abnormalities that can vary in severity and cause.
Causes of Anterior Knee pain:
Anterior knee pain usually occurs when patella (Knee cap) rubs against the lower part of the femur (thigh bone). This may occur because:
- The patella is in an abnormal position
- There is tightness or weakness of thigh muscles
- Activities which put extra pressure on patella such as running, squatting, jumping and twisting etc
- Core muscle weakness
- Flat feet.
Symptoms:
Many factors can cause anterior knee pain. Most of the following are:
- Structural Or Anatomical Abnormalities,
- Muscle Weakness,
- Tightness, Or Imbalances,
- Overuse Or Repetitive Use of The Knee,
- Can Lead to Patellofemoral Instability And Patellar Fracture.
Anterior knee pain can be nonspecific, and other similar conditions affecting the knee may cause overlapping symptoms. A doctor will conduct a thorough medical history and physical examinations to pinpoint the painful area and determine which structure is likely injured. They may also ask the person to do a single leg squat or walk around to assess for core stability, muscle imbalances, and functional limitations.
Diagnostic Tools:
The symptoms of anterior knee pain might be vague, and they may overlap with those of other knee disorders that are comparable.A detailed medical history will be taken by a doctor before starting an examination. They might inquire about:
- Prior Operations,
- Current Activities, Or Other Signs
- Pain Intensity
Also, doctor will perform a number of physical examinations to locate the sore spot and identify the most likely damaged component. In order to duplicate the pain or rule out other reasons, this entails a number of manoeuvres or movements.
To check for core stability, muscular imbalances, and functional restrictions brought on by the anterior knee discomfort, they might also ask the patient to walk about or squat on one leg.
Doctor may request imaging, such as ultrasounds, X-rays, or MRI scans, to rule out other conditions. There are limited causes that doctors can easily distinguish with exams, history, and imaging.
Treatment:
The underlying cause will determine how to treat anterior knee pain. In general, conservative medical care and lifestyle modifications helps in pain relief.
1) Rest: Complete or relative rest needs to be given for the knee to heal. This can be done by avoiding overuse activities for the knee.
2) Ice application: This helps control inflammation and thus reduces pain in acute stages of anterior knee pain.
3) Pain Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics can be recommended in order to reduce pain and inflammation.
4)Local injections: Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that can be injected into the joint in severe cases. These injections provide pain relief by reducing inflammation.
5) Physiotherapy: Application of certain therapeutic modalities like ultrasound, IFT, helps to reduce pain and swelling around the knee. Patellar mobilization and knee joint mobilization techniques performed by the physical therapist help to correct patellar mal-tracking.
6) Exercises:Stretching and strengthening exercises, especially for your quadriceps muscles is important as the patellar movement needs to be steady. Few exercises include:
In acute stage:
- Quadriceps isometric contractions
- Hamstrings isometric contractions
- Gluteal isometric contractions
- Heel slides
- Single leg raises
- Hamstring stretch
In sub-acute to chronic stage:
- Hamstring stretch
- Quadriceps stretch
- Calf stretch
- Iliotibial band stretch
- Hamstring curls
- Mini Squats to full squats
- Lunges
- Step up- step down
7)Braces: Using patellar support like knee straps, open patella knee sleeves or hinged knee braces can be used. In case of foot disorders like flat feet or high arches, foot insoles can be used in order to reduce the pressure on the knee.