All you need to know about Cluneal Neuralgia
The word "neuralgia" refers to a severe stabbing or burning sensation with the length of the nerve and “cluneal” means pertaining to the buttocks.
Chronic discomfort in the lower back region due to irritation or compression of the cluneal nerves is known as cluneal neuralgia. Even though it's not very frequent, it can greatly impact someone's quality of life. This blog will look at Cluneal Neuralgia's causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatments.
What are Cluneal Nerves?
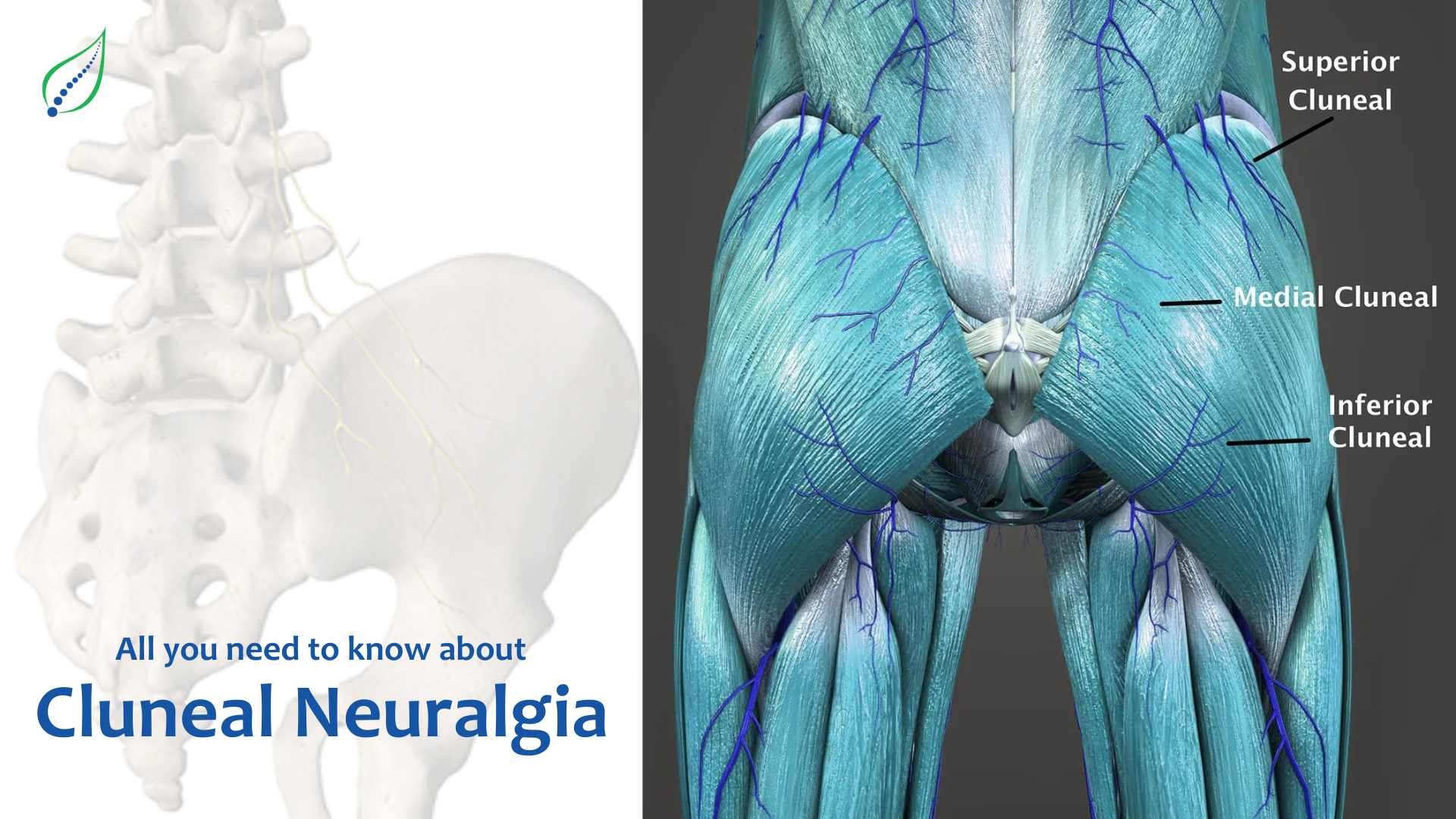
A network of nerves known as the cluneal nerves runs from the lower back to the buttock region. Their three primary branches are the Superior, medial, and inferior cluneal nerves. These nerves transmit feeling to the skin and muscles in the buttocks, upper thighs, and lower back.
.jpg)
Causes of Cluneal Neuralgia
Numerous things can lead to cluneal neuralgia, such as:
a) Nerve Entrapment: Cluneal nerve compression or entrapment can occur when they travel through small gaps in the muscles, ligaments, or fascia of the lower back and buttocks.
b) Trauma: Damage to the cluneal nerves caused by trauma or injury to the lower back, such as a fall or accident
c) Post-surgical complications: Cluneal Neuralgia can develop in some situations due to scar tissue formation or nerve injury after lower back surgery
Symptoms of Cluneal Neuralgia
Cluneal Neuralgia is characterized by persistent, localized lower back discomfort that spreads to the buttocks, hips, or thighs. Other typical signs could be:
a) Shooting or stabbing pain: This pain might be scorching, electric-like, or acute.
b) Hypersensitivity: The impacted area may develop a heightened sensitivity to pressure, warmth, and touch.
c) Numbness or tingling: In the affected area, some people may feel numbness or tingling.
d) Muscular weakness: Prolonged discomfort and decreased muscular use might result in severe cases of muscle weakening or atrophy.
Diagnosis of Cluneal Neuralgia
Cluneal neuralgia can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms frequently coincide with those of other diseases. The diagnostic procedure could entail the following:
a) Medical history and physical examination: A physical examination and evaluation of your medical history will be conducted to determine the nature and location of your pain.
b) Diagnostic injections: Local anaesthetics are administered into regions near the cluneal nerves to see if the discomfort is alleviated, validating the diagnosis.
c) Imaging tests: To rule out other underlying causes of lower back pain and to assess the cluneal nerves, X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans may be prescribed.
Treatment options for Cluneal Neuralgia
The goals of Cluneal Neuralgia treatment are to reduce pain and enhance the quality of life. The following therapies may be suggested:
a) Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, or anticonvulsants may be recommended to treat pain and reduce inflammation.
b) Physical therapy: Specific exercises, stretches, and manual treatment methods can aid in increasing flexibility, easing tension in the muscles, and relieving pain.
c) Nerve Blocks: Local anaesthetic or steroid injections near the cluneal nerves may minimize swelling and offer momentary pain relief.
d) Radiofrequency Ablation: To selectively kill the cluneal nerves and provide long-lasting pain relief, radiofrequency ablation may be suggested in some circumstances.
Self-care and lifestyle changes
Self-care practices can supplement medical interventions in the therapy of Cluneal Neuralgia. Think about the following:
a) Maintaining good posture: Using ergonomics and excellent posture helps lessen pain in the lower back.
b) Consistent exercise: Low-impact activities like walking or swimming can help strengthen the muscles that support the lower back.
c) Heat and cold therapy: Using hot or cold compresses on the injured area might help reduce pain and swelling.
d) Stress management: Stress can make it harder to feel pain; therefore, it may be helpful to incorporate stress-relieving practices like deep breathing exercises or meditation.
Chronic lower back pain that considerably limits daily activities can be brought on by cluneal neuralgia. It's important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and the best course of therapy if you have persistent lower back pain and other radiating symptoms. People with Cluneal Neuralgia can effectively manage their symptoms and enhance their overall quality of life with the correct treatment, which includes medication, physical therapy, and self-care.
_1744793045.png)
_1743751136.png)
_1738219992.png)
